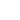
Technical Analysis: Symmetrical Triangle
In the dynamic world of trading, understanding market patterns is a cornerstone of sound decision-making. Among the many chart formations that guide traders, the symmetrical triangle stands out as a key indicator of market consolidation and potential breakout opportunities. This formation often reflects a temporary pause before a decisive move in either direction. By leveraging the educational resources and trading tools available at PlexyTrade.com, you can strengthen your ability to interpret and apply this pattern effectively.
In this article, we’ll explore what symmetrical triangles are, why they matter in technical analysis, and how you can integrate them into your trading strategy to enhance decision-making and timing.
Understanding Symmetrical Triangles
Definition and Characteristics
A symmetrical triangle is a chart pattern formed by two converging trendlines—one sloping downward and the other upward. The upper trendline connects a series of lower highs, while the lower trendline links a series of higher lows. This formation usually develops over several weeks or months, signaling a period of market consolidation as price movement becomes increasingly restricted.
For the pattern to be considered valid, traders generally look for at least two touches on each trendline and a minimum of five price swings within the triangle. These touches highlight the ongoing tug-of-war between buyers and sellers, tightening the price range as the pattern evolves.
Formation Process
As the symmetrical triangle forms, supply and demand reach equilibrium, causing price fluctuations to narrow. This compression reflects market indecision—neither buyers nor sellers dominate, leading to declining volatility. During this time, trading volume typically decreases, signaling a lack of conviction among participants.
This quiet phase often precedes significant movement. When the balance finally tips—whether upward or downward—the breakout tends to occur with a sharp increase in volume, confirming renewed momentum and direction.
Significance in Technical Analysis
Market Psychology Behind Symmetrical Triangles
The symmetrical triangle is more than a geometric shape—it’s a reflection of market psychology. It represents a standoff between bullish and bearish sentiment. As each side tests the other, price movement contracts and tension builds. This “calm before the storm” often results in an explosive breakout once the market chooses a direction.
For traders, recognizing this buildup of pressure is critical. The pattern’s neutrality means it can signal either a continuation or a reversal of the prior trend, depending on where the breakout occurs.
Identifying the Trend and Volume
To identify a symmetrical triangle, draw trendlines connecting the key swing highs and lows until they converge. Watch volume closely—declining volume during consolidation suggests weakening participation, while a volume surge at breakout often validates the move. Traders who monitor both price structure and volume dynamics are better positioned to act decisively when opportunity arises.
Trading Strategies Using Symmetrical Triangles
Entry and Exit Points
Effective trading with symmetrical triangles hinges on precise entry and exit timing. The ideal entry occurs on a confirmed breakout:
- Bullish breakout: when price closes above the upper trendline.
- Bearish breakout: when price drops below the lower trendline.
A breakout should be supported by a clear rise in volume to confirm authenticity. To determine a price target, measure the vertical height of the triangle’s base and project that distance from the breakout point—this provides a reasonable estimate of potential movement.
Stop Loss Placement
Risk management is crucial for maintaining long-term success. When setting a stop-loss, place it just inside the opposite side of the triangle from your entry point. This placement allows for normal market fluctuations while protecting against false breakouts.
PlexyTrade encourages traders to prioritize disciplined risk control as part of every strategy—consistent protection against downside risk is the foundation of sustainable trading performance.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Analyzing Historical Data
Symmetrical triangles can be found across a wide range of markets and trading instruments, from forex and commodities to stocks and indices. A look at historical market data shows that these formations tend to be more reliable when accompanied by strong volume confirmation at the breakout point.
While false breakouts are not uncommon, understanding how volume behavior interacts with price movement can greatly improve trading outcomes. Experienced traders often pay close attention to sudden volume spikes, as these can serve as powerful signals that the market is ready to move decisively.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Despite their effectiveness, symmetrical triangles are often misinterpreted by traders. One of the most common errors is confusing them with pennants or flag patterns, which represent short-term continuation setups rather than longer consolidation phases.
Another frequent mistake is entering a trade too early—before the breakout has been confirmed—or neglecting to consider volume cues. Acting prematurely or overlooking key confirmation signals can lead to false entries and potential losses.
By remaining patient and disciplined, and by leveraging PlexyTrade’s analytical tools and educational insights, traders can avoid these pitfalls and make more informed, confident trading decisions.
Conclusion
The symmetrical triangle represents more than a pause in price movement—it’s a snapshot of market tension and opportunity. By learning to recognize this pattern, confirm breakouts with volume, and apply disciplined entry and exit strategies, traders can capitalize on momentum shifts with confidence.
At PlexyTrade, we’re dedicated to helping traders turn technical knowledge into practical skill. With the right insights and tools, every pattern on the chart can become a step toward smarter, more informed trading decisions.